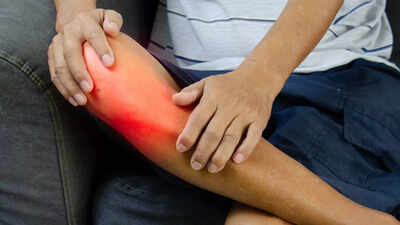
Having sudden, widespread joint pain can be alarming, but you are not alone. Joint pain, medically known as arthralgia, occurs when one or more joints are inflamed, damaged, or affected by underlying health conditions.According to MedicalNewsToday, causes can vary from immediate concerns like a viral illness or minor injury to chronic conditions. Inflammation can cause pain based on an infectious process, crystal or mineral deposits, or immune system problems. This causes swelling, stiffness, and often pain. Overuse or past trauma, or general ageing and wear and tear, can also cause pain. The underlying cause must be identified to give you the most effective treatment and pain relief.
10 potential causes of sudden joint pain
Flu: Flu is a common infectious illness caused by influenza viruses, with symptoms like severe muscle or body aches, along with fever, chills, cough, sore throat, running nose, and sometimes vomiting or diarrhoea, especially in children. While most people recover within two weeks without medical treatment, adults over 65, young children, pregnant women, and those with chronic conditions like asthma or diabetes are at higher risk for complications.
COVID-19: COVID-19 can cause muscle or body aches along with symptoms such as fatigue, fever, chills, headache, cough, sore throat, shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea. Most people have mild to moderate symptoms and recover without treatment. However, serious complications such as blood clots, heart failure, and neurological issues can occur. Higher-risk groups include adults over 65, unvaccinated individuals, people with chronic illnesses, and those with weakened immune systems.
Post-Viral Complications: While many recover fully from common respiratory viruses, some people experience symptoms lasting weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection, including joint pain. Post-viral conditions include- post-viral syndrome, long COVID, and reactive arthritis. Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS): This is a chronic condition that can develop after a viral illness, though sometimes no trigger is identified.
Common symptoms are joint pain without swelling, muscle aches, and headaches. Other signs include flu-like symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes, difficulty sleeping, cognitive issues known as “brain fog,” dizziness upon standing, and post-exertional malaise, where symptoms worsen suddenly after physical or mental activity.Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which leads to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints.
This results in sudden inflammation, swelling, and intense pain, often affecting a single joint like the big toe. Gout attacks usually peak within 12 to 24 hours after symptoms begin. Autoimmune Conditions: Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to joint inflammation and pain. Common autoimmune conditions that affect the joints include:Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chronic inflammation causing joint pain, stiffness, and swelling; managed with medication, therapy, and exercise to prevent damage.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chronic inflammation causing joint pain, stiffness, and swelling; managed with medication, therapy, and exercise to prevent damage.
- Lupus: Autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs; treatments manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Affects 20% of psoriasis patients, causing joint inflammation; treated with medication, therapy, and exercise.
Also read | 10 common heart health myths that you must know

 8 hours ago
35
8 hours ago
35

























 English (US)
English (US)