- close
01/11The human body needs 360-410 mg of magnesium on a daily basis
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous physiological functions within the human body. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, contributing to various aspects of health, from maintaining strong bones to supporting heart function and even influencing mood and mental well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of magnesium and its various roles in maintaining overall health.
02/11It metabolizes important nutrients
Magnesium is a cofactor in enzymatic reactions responsible for metabolizing nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It aids in the conversion of food into energy and helps the body efficiently utilize the calories it receives. The body's primary source of energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), requires magnesium for its synthesis. Without adequate magnesium, energy production can be compromised, leading to fatigue and reduced physical performance.
03/11It keeps the bones healthy
Magnesium is essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. It works in conjunction with calcium and vitamin D to promote bone mineralization and structure. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
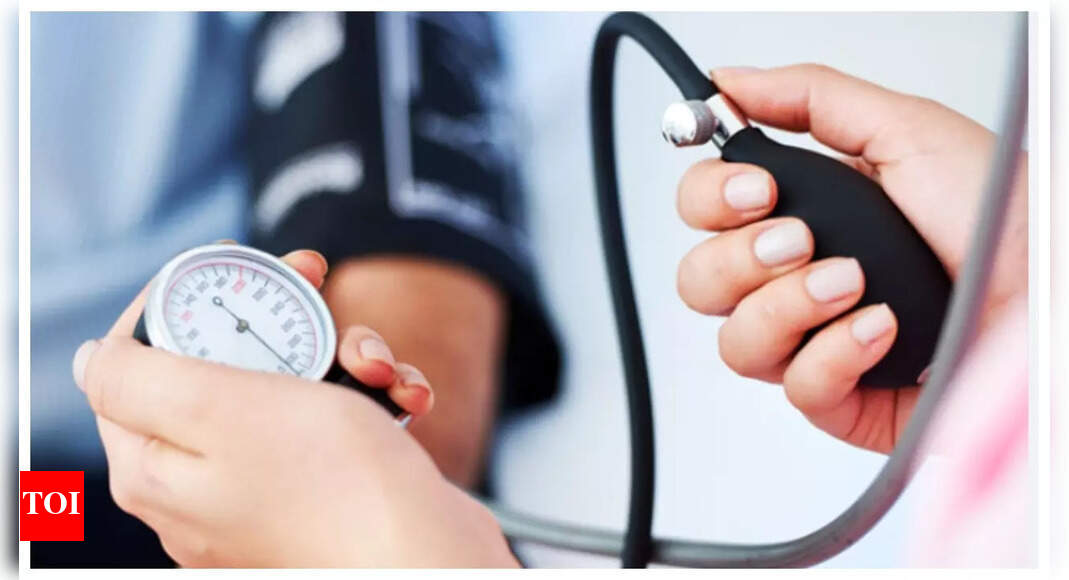
04/11It keeps the heart healthy
Magnesium plays a crucial role in heart health. It helps regulate blood pressure, as it influences the dilation and constriction of blood vessels. Adequate magnesium levels are associated with a reduced risk of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
05/11It helps in muscle contraction and relaxation
Muscles, including the heart, rely on magnesium for proper function. It is essential for muscle contractions and relaxation. A deficiency can result in muscle cramps, weakness, and irregular heart rhythms.
06/11It aids in nerve function
Magnesium is involved in transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscles. It helps regulate neurotransmitters and is critical for overall nervous system function. Low magnesium levels may lead to symptoms like tingling, numbness, and muscle spasms.
07/11Magnesium helps in protein formation
Magnesium plays a key role in protein formation, which is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body. It is particularly crucial for the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
08/11It boosts immune system
Adequate magnesium levels are associated with a well-functioning immune system. It can help the body defend against infections and illnesses.
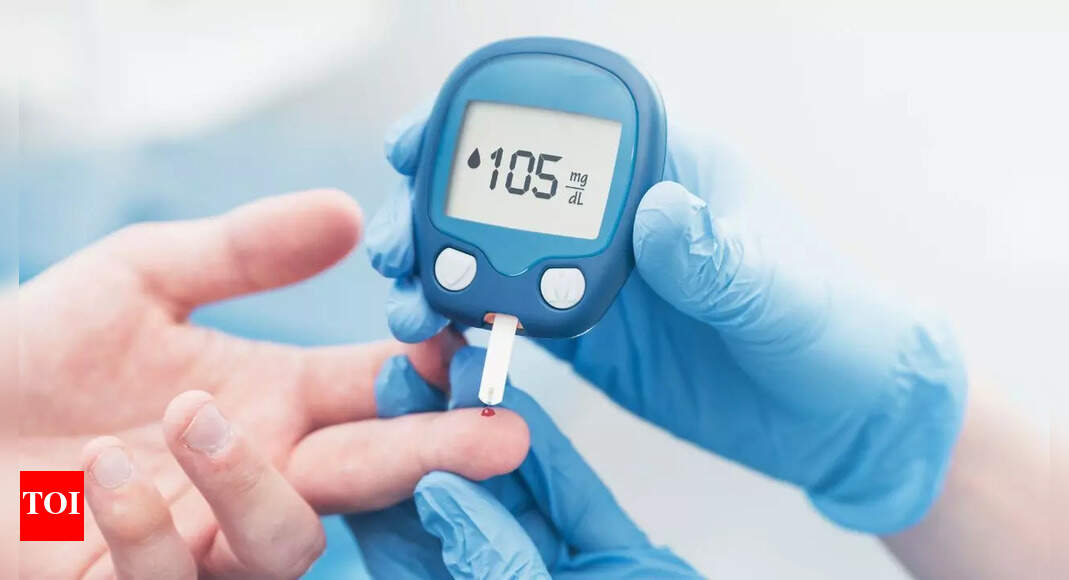
09/11It metabolizes glucose
Magnesium influences insulin release and glucose uptake by cells. It plays a role in glucose metabolism and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Low magnesium levels have been linked to insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
10/11It improves mood
There is growing evidence that magnesium may have an impact on mental health and mood regulation. It is involved in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and may play a role in conditions such as depression and anxiety. Some studies suggest that magnesium supplementation may help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
11/11Magnesium deficiency affects the body in several ways
Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is not uncommon, and many people do not consume adequate amounts of this mineral in their diets. Factors such as poor dietary choices, certain medical conditions, medications, and excessive alcohol intake can contribute to magnesium deficiency. Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can vary and may include muscle cramps, muscle weakness, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, abnormal heart rhythms, and numbness or tingling. Severe magnesium deficiency can lead to more serious health issues, including seizures and abnormal heart rhythms.

 1 year ago
402
1 year ago
402


























 English (US)
English (US)